YOLOv8 Webcam Detection
Build a full-screen real-time object detection app with YOLOv8, MJPEG streaming, and a React frontend on WendyOS
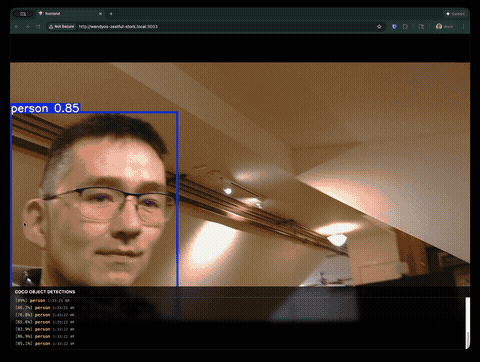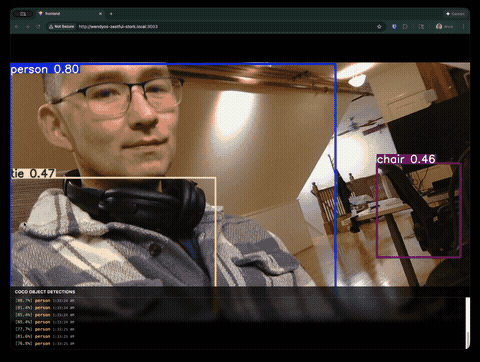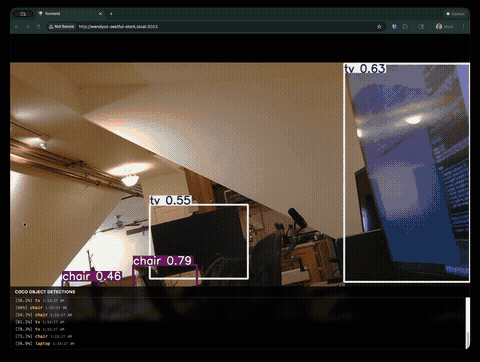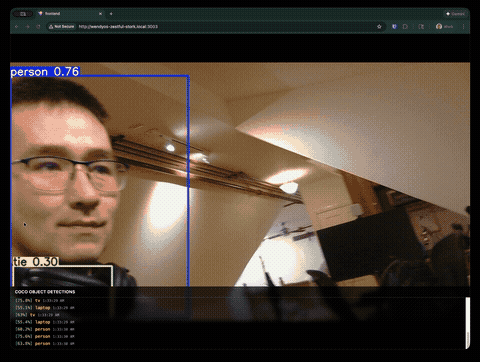
Real-Time COCO Object Detection with YOLOv8
This guide walks you through building a complete webcam detection application that runs YOLOv8 on a WendyOS device. The app features a full-screen video feed with bounding box overlays and a detection log showing identified objects from the COCO dataset (80 classes including people, cars, animals, and everyday objects).
The complete sample is available in the samples repository.
What You'll Build
- A FastAPI backend that captures webcam frames and runs YOLOv8 inference
- MJPEG video streaming with detection overlays drawn by YOLOv8
- A React + Tailwind frontend with full-screen video and a detection log overlay
- A Docker container optimized for NVIDIA Jetson devices
Prerequisites
- Wendy CLI installed on your development machine
- Docker installed (see Docker Installation)
- A WendyOS device (NVIDIA Jetson Orin Nano, Jetson AGX, etc.)
- A USB webcam connected to your WendyOS device
Recommended Webcams: See our Buyers Guide for webcam recommendations including the Logitech C920 and C270.
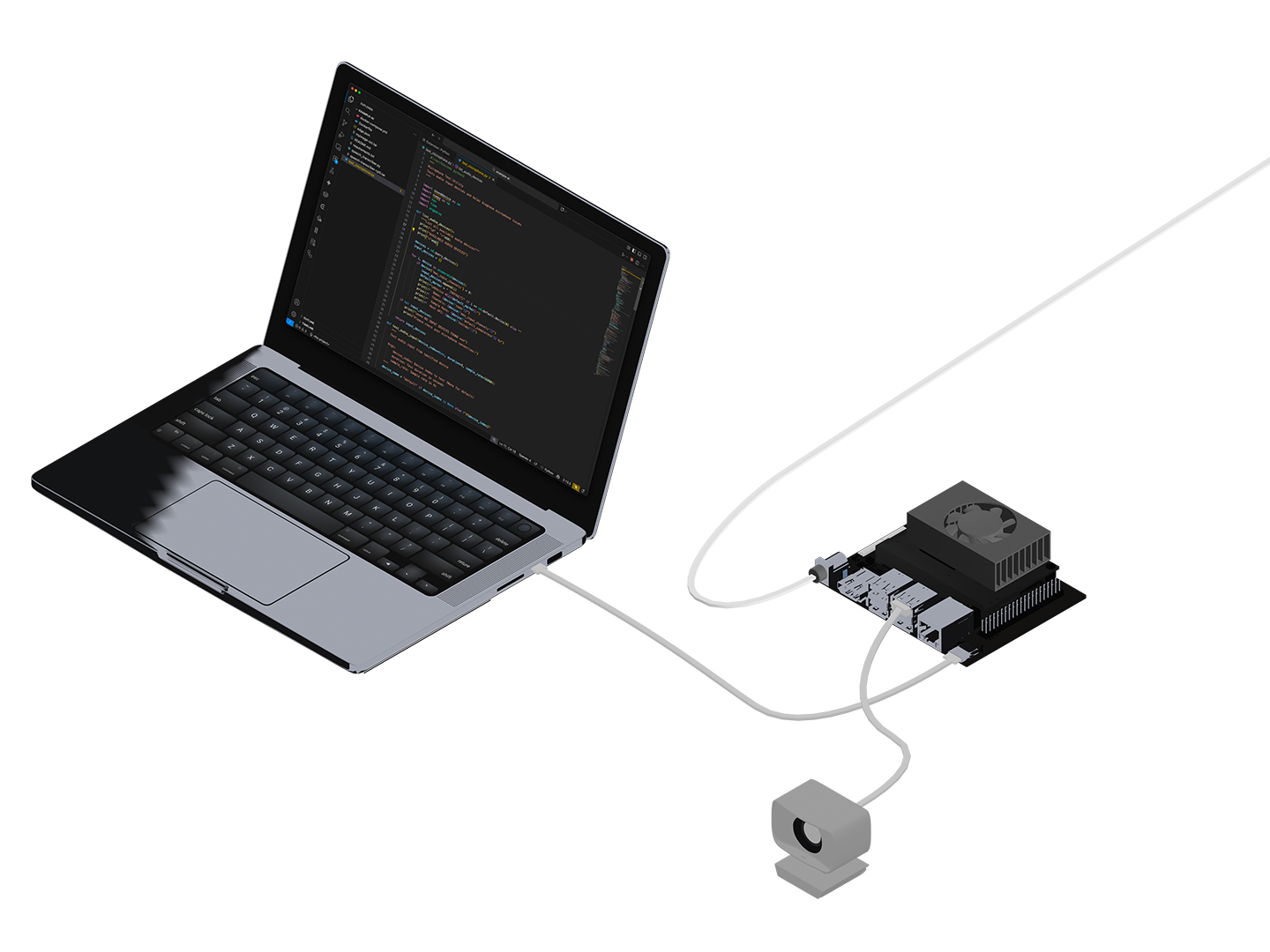

Understanding the Architecture
This sample uses a prebuilt Ultralytics Docker image specifically optimized for Jetson devices. The ultralytics/ultralytics:latest-jetson-jetpack6 image comes with:
- YOLOv8 and the Ultralytics library pre-installed
- OpenCV with CUDA support
- PyTorch optimized for Jetson GPUs
- All necessary CUDA libraries
This means you don't need to compile OpenCV or PyTorch from source - saving significant build time.
Large Image Size: The Ultralytics Jetson image is approximately 5-9 GB in size. Initial uploads to your device can be slow depending on your network connection. See the Speeding Up Uploads section for tips.
Project Structure
yolov8/
├── Dockerfile
├── wendy.json
├── server/
│ └── app.py
└── frontend/
├── package.json
├── src/
│ ├── App.tsx
│ └── main.tsx
└── ...Clone the Sample
The easiest way to get started is to clone the samples repository:
git clone https://github.com/wendylabsinc/samples.git
cd samples/python/yolov8Understanding the Dockerfile
The Dockerfile uses a multi-stage build:
# Build frontend
FROM node:22-slim AS frontend-builder
WORKDIR /app/frontend
COPY frontend/package*.json ./
RUN npm ci
COPY frontend/ ./
RUN npm run build
# Runtime stage - Ultralytics official Jetson image
FROM ultralytics/ultralytics:latest-jetson-jetpack6
WORKDIR /app
# Only need to install web server dependencies
RUN pip3 install --no-cache-dir fastapi "uvicorn[standard]"
# Pre-download the YOLOv8 model during build (so it works offline)
RUN python3 -c "from ultralytics import YOLO; YOLO('yolov8n.pt')"
# Copy server files
COPY server/app.py ./
# Copy the built frontend
COPY --from=frontend-builder /app/frontend/dist ./frontend/dist
ENV FRONTEND_DIST=/app/frontend/dist
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1
EXPOSE 3003
CMD ["uvicorn", "app:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "3003"]Key points:
- The first stage builds the React frontend with Node.js
- The second stage uses the prebuilt Ultralytics Jetson image
- The YOLOv8 model (
yolov8n.pt) is downloaded during build, not at runtime - This ensures the app works even if the device has no internet access
Understanding the Backend
The FastAPI backend (server/app.py) handles webcam capture, YOLOv8 inference, MJPEG streaming, and detection logging:
from collections import deque
from datetime import datetime, timezone
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.responses import StreamingResponse
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
app = FastAPI()
# Load YOLOv8 model (pre-downloaded in Docker build)
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
# Store recent detections for the log
detection_log: deque = deque(maxlen=100)
def generate_frames():
"""Generate MJPEG frames with YOLOv8 detection overlay."""
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 1280)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 720)
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# Run YOLOv8 inference
results = model(frame, verbose=False)
# Log detections with confidence > 50%
timestamp = datetime.now(timezone.utc).isoformat()
for result in results:
for box in result.boxes:
conf = float(box.conf[0])
if conf > 0.5:
cls_name = model.names[int(box.cls[0])]
detection_log.append({
"label": cls_name,
"confidence": round(conf * 100, 1),
"timestamp": timestamp
})
# Draw bounding boxes and encode as JPEG
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
_, buffer = cv2.imencode('.jpg', annotated_frame,
[cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY, 80])
yield (b'--frame\r\n'
b'Content-Type: image/jpeg\r\n\r\n' +
buffer.tobytes() + b'\r\n')
@app.get("/api/video-feed")
async def video_feed():
"""Stream MJPEG video with YOLOv8 detections."""
return StreamingResponse(
generate_frames(),
media_type="multipart/x-mixed-replace; boundary=frame"
)
@app.get("/api/detections")
async def get_detections():
"""Get recent detections for the log overlay."""
return list(detection_log)[-20:]How it works:
generate_frames()captures webcam frames and runs YOLOv8 inferenceresults[0].plot()draws bounding boxes directly on the frame- Detections above 50% confidence are logged with label, confidence, and timestamp
/api/detectionsreturns the last 20 detections for the frontend overlay
Understanding the Frontend
The React frontend (frontend/src/App.tsx) displays a full-screen video feed with a detection log overlay:
import { useState, useEffect, useRef } from "react";
interface Detection {
label: string;
confidence: number;
timestamp: string;
}
function App() {
const [detections, setDetections] = useState<Detection[]>([]);
const logRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
useEffect(() => {
// Poll for detections every 500ms
const fetchDetections = async () => {
const response = await fetch("/api/detections");
const data: Detection[] = await response.json();
setDetections(data);
};
fetchDetections();
const interval = setInterval(fetchDetections, 500);
return () => clearInterval(interval);
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
// Auto-scroll to bottom of log
if (logRef.current) {
logRef.current.scrollTop = logRef.current.scrollHeight;
}
}, [detections]);
return (
<div className="relative h-screen w-screen overflow-hidden bg-black">
{/* Full-screen video feed */}
<img
src="/api/video-feed"
alt="YOLOv8 Detection Feed"
className="absolute inset-0 h-full w-full object-contain"
/>
{/* Bottom overlay for detection log (1/5 of screen) */}
<div className="absolute bottom-0 left-0 right-0 h-1/5
bg-black/70 backdrop-blur-sm z-10">
<div className="h-full flex flex-col">
<div className="px-4 py-2 border-b border-white/20">
<h2 className="text-white text-sm font-semibold uppercase">
COCO Object Detections
</h2>
</div>
<div ref={logRef}
className="flex-1 overflow-y-auto px-4 py-2 font-mono text-sm">
{detections.map((detection, index) => (
<div key={`${detection.timestamp}-${index}`}
className="text-white/90 py-0.5">
<span className="text-green-400">
[{detection.confidence}%]
</span>{" "}
<span className="text-yellow-300">
{detection.label}
</span>{" "}
<span className="text-white/50 text-xs">
{new Date(detection.timestamp).toLocaleTimeString()}
</span>
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default App;UI Features:
- Full-screen MJPEG video feed via a simple
<img>tag - Semi-transparent overlay at the bottom (1/5 of screen height)
- Detection entries show confidence in green, label in yellow, time in gray
- Auto-scrolls to show the latest detections
Configure Entitlements
The wendy.json file specifies the required device permissions:
{
"appId": "com.example.python-yolov8",
"version": "0.0.1",
"entitlements": [
{ "type": "network", "mode": "host" },
{ "type": "gpu" },
{ "type": "video" }
]
}- network (host mode): Allows binding to ports directly on the device
- gpu: Enables CUDA acceleration for YOLOv8 inference
- video: Grants access to
/dev/video*webcam devices
Deploy to Your Device
Connect your USB webcam to the Jetson, then run:
wendy runThe CLI will:
- Build the Docker image (cross-compiling for ARM64)
- Push the image to your device's local registry
- Start the container with the configured entitlements
wendy run
✔︎ Searching for WendyOS devices [5.0s]
✔︎ Which device?: wendyos-zestful-stork.local [USB, LAN]
✔︎ Builder ready [0.2s]
✔︎ Container built and uploaded successfully! [45.2s]
✔ Success
Started app
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:3003Open your browser to:
http://wendyos-zestful-stork.local:3003Replace the hostname with your device's actual hostname.
Speeding Up Uploads
The Ultralytics Jetson image is large (5-9 GB), which can make initial deployments slow over Wi-Fi.
Use USB-3 Direct Connection
For the fastest uploads, connect your laptop directly to the Jetson via USB-C:
- Use a USB 3.0 or USB-C cable (not USB 2.0)
- The Wendy CLI will automatically detect the USB connection
- Uploads over USB are significantly faster than Wi-Fi or Ethernet
# The CLI will show [USB] when connected via USB
wendy discover
╭─────────────────────────────────────┬───────────────────╮
│ Device │ Connection │
├─────────────────────────────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ wendyos-zestful-stork.local │ USB, LAN │
╰─────────────────────────────────────┴───────────────────╯Subsequent Deploys Are Fast
Docker layer caching means that after the initial upload:
- Only changed layers are uploaded
- Code changes typically upload in seconds
- The large base image layers are cached on the device
Troubleshooting
Next Steps
- Modify the detection filter in
app.pyto only show specific object classes - Add audio alerts when certain objects are detected
- Implement recording of detection events to a database
- Try different YOLOv8 model sizes (
yolov8s.pt,yolov8m.pt) for better accuracy